
Host A had an IP of 192.168.30.1 and was on port 1.
Extreme switch show mac address table mac#
Total Mac Addresses for this criterion: 3 The hosts could ping each other and the MAC address-table was as follows:ģ750-1#show mac address-table dynamic vlan 30 I configured a switch with three hosts directly connected on VLAN 30. This isn’t an easy thing to replicate so please forgive the artificial nature of the lab.
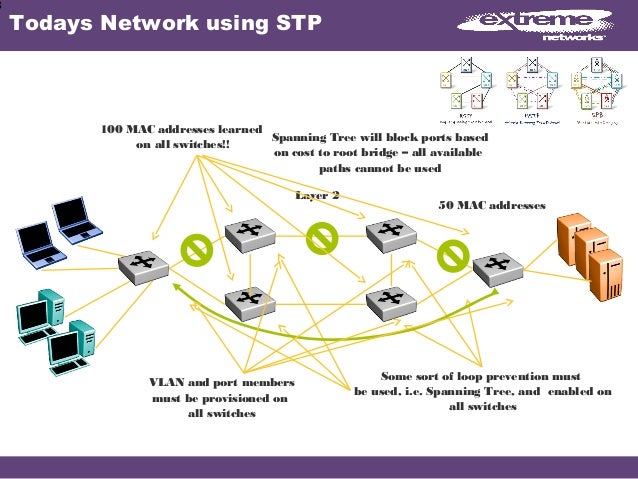

What happens when B tries to send A a frame now? The switch won’t flood the frame as it knows a destination and it won’t send the frame back down the link – it gets dropped. Host in vlan A is flapping betweenĪnd the MAC address-table would become: Port Host If the switch were to then receive a frame on port 0/2 with a source MAC address of aaaa, there would be clash and the switch would log something like this: 1664321: Nov 14 11:18:16 UTC: %MAC_MOVE-SP-4-NOTIF: When B replies the MAC address table becomes: Port HostĪnd the switch forwards the frame to port 0/1 – there is no need to flood now since the location of A is known. The switch populates it MAC address-table something like: Port HostĪnd floods the frame out of all other ports. Assume A is on port 0/1 and B is on port 0/2. Say a device ‘A’ with MAC (hereafter aaaa) sends a frame to device ‘B’ with MAC address bbbb. Switches learn where hosts are by examining the source MAC address in frames received on a port, and populating its MAC address-table with an entry for that MAC address and port. If this makes no sense, perhaps a quick summary of how switching at layer 2 works will help. A WAP must translate the Wi-Fi frames into ethernet frames, and vice versa, but it preserves the original host source and destination MAC addresses of the original frames on the translated frames.A MAC Flap is caused when a switch receives packets from two different interfaces with the same source MAC address. Bridges normally forward frames transparently. The bridges will not normally have MAC address table entries for other bridges because the bridges do not originate traffic, so the frames will not have the source MAC address associated with the bridge. The switch interface for the WAP could have multiple MAC addresses associated with it in the switch MAC address table if multiple hosts on the WAP send frames into the switch, but the key is that the switch must see at least one frame for a host enter the switch during its timeout period for you to see the MAC address in its MAC address table. It is only when a host on the WAP sends a frame that enters the switch that the switch will create an entry for the MAC address of the host. If a host on your WAP sends frames to another host on the WAP, the switch will not see those frames, so it will not have an entry in its MAC address table for those hosts. In your comment, you explain that you have another bridge (switches and WAPs are bridges). On a Cisco switch, the show mac-address-table command will show all the entries for all the MAC address tables, but other vendors may do it differently.Īlso, MAC address table entries will time out, so if the switch has not seen any frames from a particular host in a while, the MAC address table entry for that host will time out of the table.
Extreme switch show mac address table how to#
You did not specify the switch model, so we cannot tell you specifically how to see the MAC address table. A switch has a MAC address table for each VLAN, and the switch will populate the MAC address table of the VLAN with the source MAC address of any frame entering the switch on an interface in that VLAN.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
